- Discussion:
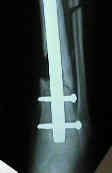
- by definition involves a tibia fracture infection that has gone on to non union;
- by definition, infected non union is a Cierney IV osteomyelitis, meaning that the fracture is
unstable before and after the debridement;
- infected non union is a relative contraindication to internal fixation across the frx;
- tibial nonunions should never be approached thru a previously infected scar;
- instead plan lateral or posterior approaches, avoiding as much as possible the ends of long bones,
& roughening normal parts of bone;
- large iliac grafts may be placed between the tibia and fibula
- reference:
- Infected nonunion of the long bones.
- Work Up:
- an infected delayed union requires débridement, soft-tissue coverage, bone stabilization and bone-grafting;
- radiographs:
- attempt to determine from x-rays, how much bone needs to be debrided;
- plan for hardware removal;
- bone scan: indium scan: may offer higher specificity;
- CBC, sed rate, CRP;
- reference:
- Diagnosis of infection in ununited fractures. Combined imaging with indium-111-labeled leukocytes and technetium-99m methylene diphosphonate.
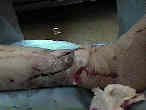
- Initial Management:
- debridement of sequestrum
- the most important element in debridement to remove a sequestrum and other devitalized tissue;
- in some cases there may be an obvious sequestrum with an associated draining sinus;
- consider making small anterolateral incision (over anterior compartment) inorder to reach
and debride sequestrum, and consider reaming the IM canal inorder to debride the
rest of the canal;
- following the osseous debridement, the skin drainage will often resolve, thus preventing the need
for soft tissue coverage;
- consider need for antibiotic bead application;
- hardware: controversies:
- references:
- Treatment of infection after fracture fixation. Opinion: two-stage protocol: treatment of nonunion after treatment of infection.
- Treatment of infection after fracture fixation. Opinion: retain stable implant and suppress infection until union.
- soft tissue coverage:
- see contaminated wound care and wound vac);
- preoperatively, determine whether there will be a need for extensive soft tissue debridement;
- excision of draining sinuses, ect), which might in some cases require application of a free flap;
- note that following debridement of sequestrum, the draining sinus will often spontaneously resolve;
- references:
- Closure of the skin defect overlying infected non-union by skin traction.
- Tibial Stabilization:
- intramedullary nailing:
- references:
- Antibiotic cement-coated interlocking nail for the treatment of infected nonunions and segmental bone defects.
- Treatment of infected pseudarthrosis of the femur and tibia with an interlocking nail.
- Treatment of infected nonunion and delayed union of tibia fractures with locking intramedullary nails.
- circular wire fixators:
- a simple hybid fixator can be applied, if the goal is to merely obtain bony union;
- if there has been tibial shortening (from frx debridement), then limb lengthening can be considered once there is frx union;
- ilizarov technique:
- this statedegy involves potential for simultaneous compression of the frx site along with lengthening of the opposite metaphysis
(to compensate for the shortening brought about from debridement);
- when Ilizarov is used in conjunction w/ radical resection and distraction histiogenesis, the majority of patients can expect at
least one minor complication;
- bone union averages 6 months once intercalary segments come into contact;
- reference:
- Use of the Ilizarov technique for treatment of non-union of the tibia associated with infection.
- Fracture Healing and Restoration of Length: (see managment of tibia fracture defects)
- tibial lengthening
- bone morphogenic proteins
- posterolateral bone grafting:
- can be used to avoid significant shortening;
- whenever possible, posterolat. graft via virgin approach is used to avoid subjecting previously traumatized area to more insult;
- has been successful in treating infected non-unions & can be performed w/o disturbing anteromedial soft tissue defects;
- contraindicated a fibulectomy has been performed previously;
- induced membrane technique
- papineau technique
- references:
- Results of bone grafting for infected tibial nonunion.
- Treatment of infected non-unions and segmental defects of the tibia with staged microvascular muscle transplantation and bone-grafting.
Non-vascularised fibular transfer in the management of defects of long bones after sequestrectomy in children.
The infected nonunion of the tibia.
Results of vancomycin-impregnated cancellous bone grafting for infected tibial nonunion.
Infected nonunion of the long bones.
Nonunion of the diaphysis of long bones.
Management of infected nonunion of long bones: The last decade (1996-2006).

