- See:
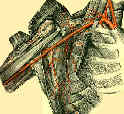
- Arteries of the Upper Limb;
- Profunda Brachi;
- Anatomy:
- brachial artery originates at the lateral border of teres major muscle & courses down anterior humerus posterior to bicipital aponeurosis;
- brachial artery has three main braches, of which profunda brachi is first and most important;
- superior and inferior ulnar collateral arteries are the other two;
- branches into radial & ulnar artery below antecubital fossa;
- about 1 inch below antecubital fossa, brachial artery divides into radial & ulnar artery, w/ latter being larger;
- about 1 inch below the origin of the ulnar artery, the common interosseous artery arises and subsequently divides into an anterior or
volar branch and posterior or dorsal branch;
- Injury to Brachial Artery:
- brachial vessels are commonly injured from both penetrating and blunt trauma usually associated with humeral fractures;
- artery is at greatest risk in proximal one-third, where it lies next to humeral shaft, & in distal one-third near the elbow;
- degree of ischemia after brachial artery injuries depends on whether injury is proximal or distal to profunda brachi ;
- there is a 2 fold increase in amputation if the brachial artery was ligated proximal to the profunda brachi;
- there are anastomoses around elbow from inferior ulnar collateral artery above to branches of the ulnar artery below;
- if collateral circulation is inadequate, obstruction of brachial artery may be catastrophic, leading to loss of the forearm and hand;
- ligation of the brachial artery above the profuda brachii artery will result in a loss of limb in about 50% of cases;
- ligation below level of profunda brachi will result in loss of limb in 25% of cases;
- Thrombosis of Brachial Artery:
- after cardiac catheterization is well known;
- 1.5% of patients required thrombectomy and local arterial reconstruction after cardiac catheterization;
- following brachial artery thrombosis, the patients may suffer severe ischemia immediately, but they may be asymptomatic because of the extensive
collateral circulation about the elbow;
- however, surgical repair is recommended even if pt is only mildly symptomatic, as a significant number of pts develop subsequent thrombosis if left untreated;
- Laceration:
- whenever possible use saphenous vein as interpositional graft;
- there is a high incidence of thrombosis when polytetrafluoroethylene grafts are used in brachial repairs;
- do not use prosthetic grafts in small artery repairs;
- injuries of the brachial or arm veins can be treated by ligation, as edema is rare;
- w/ associated nerve injury consider cervical sympathectomy to relieve causalgia;
- Puncture of Brachial Artery: (ABG);
- in antecubital fossa, brachial artery & median nerve pass underneath lacertus fibrosus (biciptal aponeurosis);
- lacertus fibrosus forms an unyeilding band, and any hematoma or swelling in the antecubital fossa is poorly tolerated;
- compression of the brachial artery or median nerve by hematoma can result in severe ischemia or neuropathy or both;
- patients in whom the brachial artery is punctured for sampling of ABG or for a-line are at risk of developing hematoma that can compress the brachial artery,
especially if the patient is receiving anticoagulants;
- there are several dozen reports of disabling complications after brachial artery puncture;
- all necessary brachial artery punctures is done above antecubital fossa to decrease the risk of bleeding underneathe the lacertus fibrosis;
- artery is identified by palpation in the cubital fossa, on medial side of biceps tendons, & needle is inserted on line level w/ medial and lateral epicondyles,
avoiding any obvious superficial veins & also median nerve which is on medial side of artery;
- artery and nerve are both deep to the deep fascia
Scientific Papers: Traumatic Injuries of the Brachial Artery.
Vascular proximity: is it a valid indication for arteriography in asymptomatic patients
Brachial artery injury after cardiac catheterization.
The use of a shunting catheter for a ruptured brachial artery following open elbow dislocation.
Ulnar artery thrombosis: a sports-related injury
The results of radial and ulnar arterial repair in the forearm. Experience in three medical centers.
An Experience with Upper-Extremity Vascular Trauma.
Year Book: Upper Extremity Arterial Injury in Athletes.
A retrospective review of brachial artery injuries and repairs-Is it still a "training artery"?

