- See: Deep Palmar Arch
- Discussion:
- superficial arch is much larger & important than the deep arch
- classical complete arch present in only 34% (from radial & ulnar)
- variations:
- entirely from the ulnar artery in 37%
- arch incomplete in 20% of patients;
- superficial palmar branch of the ulnar artery is major source of arterial inflow for fingers of the ulnar portion of hand;
- this vessel has variable continuity w/ radial artery, usually by anastomosis with the radialis indicis or princeps pollicis artery;
- Anatomy:
- as ulnar artery passes thru Guyon's canal w/ ulnar nerve, both structures bifurcate;
- ulnar artery passes in close proximity to hook of hamate bone, then divides into the deep and superficial palmar branches;
- superficial branch courses superficial to the hypothenar muscles and proximal to the protective covering of the palmar aponeurosis;
- superficial palmar arch is terminal branch of the ulnar artery;
- it is this short segment of artery, proximal to superficial palmar arch, that is prone to damge from acute and chronic trauma to hypothenar eminence, since there is no
soft tissue protection of this segment except for skin;
- line drawn across palm at the level of the distal border of fully abducted thumb marks approximate locatation of superficial arch;
- deep arch is a finger's breath superficial;
- ulnar artery can usually be felt just lateral to pisiform;
- immediately distal to this point, artery divides into its larger branch which forms most of superficial arch & smaller branch which forms lesser part of deep palmar ;
- superficial arch gives off digital branches which bifurcate into phalangeal branches about finger's breadth proximal to web border of hand;
- superficial arch & its deep branches are immediately deep to tough central part of palmar aponeurosis and are superficial to branches of median and ulnar nerves;
- this relationship to the nerves is reversed in the fingers;
- Hypothenar syndrome:
- traumatic thrombosis of superficial palmar arch of ulnar artery resulting from repetitive use of hand as a hammer;
- in this maneuver, maximum force of blow occurs over hook hamate bone, stie of superifical palmar arch of ulnar artery

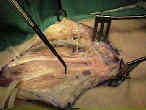
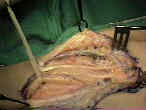
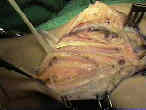

Interpositional vein grafts to restore the superficial palmar arch in severe devascularizing injuries of the hand.
Arterial System of the Fingers.
Arterial patterns in the hand based upon a study of 650 specimens.


