- Anatomy:
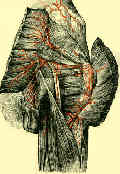
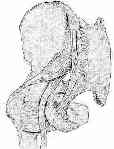
- arises from lumbrosacral plexus: L4, L5, S1, S2, S3;
- nerve emerges from pelvis below piriformis & enters thigh between ischial tuberosity & greater trochanter;
- in 10% of patients, the sciatic nerve is separated in greater sciatic foramen by all or part of the piriformis;
- sciatic nerve is accompanied by PFCN & by inferior gluteal artery and its special branch to nerve;
- nerve enters thigh beneath lower border of maximus;
- descends near middle of thigh, lying on adductor magnus muscle & being crossed obliquely by long head of biceps femoris ;
- nerve usually separates in upper part of popliteal space;
- Tibal Nerve Branch:
- from anterion branches of LS plexus: L4, L5, S1, S2, S3;
- 2 branches from tibial division: below quadratus femoris:
- upper branch passes to long head of biceps femoris & upper portion of semitendinosus;
- lower branch: innervates lower portion of semitendinosus & semimembranous & ischiocondylar portion of adductor magnus ;
- Common Peroneal Nerve:
- from posterior branches: L4, L5, S1, S2;
- nerve to short head of biceps femoris arises from lateral side of sciatic nerve (common peroneal portion) in middle of thigh & enters
superficial surface of the muscle;
- Sciatic Nerve in THR:
- protection of sciatic nerve in THR
- nerve injuries from THR
- in THR the sciatic nerve may be injured by excessive tension when extremity has been lengthened significantly, especially in pts w/ DDH ;
- sciatic nerve is at risk during leg lengthening;
- peroneal division is most often affected;
- w/ sciatic nerve injury following THR, keep pts leg flexed over side of bed;
- if injury was due to traction, the nerve may recover in the relaxed position;
- Sciatic Nerver Injury from Kocher Langenbock Approach;
- sciatic nerve palsy from Kocher Langenbock Approach;
- can be prevented by intraop monitoring of amount of tension applied by assistants retracting the nerve;
- early treatment consists of AFO
- sciatic nerve recovery may occur over a 3 yr period;
- tendon transfers are usually not performed unitl 3 yr post op
- References:
Sciatic nerve palsy after total hip arthroplasty: treatment by modular neck shortening.
Nerve palsy associated with total hip replacement. Risk factors and prognosis.
Contributory factors and etiology of sciatic nerve palsy in total hip arthroplasty.
Somatosensory-evoked potential monitored during total hip arthroplasty.
Sciatic paralysis. A complication of bleeding following hip surgery.
Paralytic drop foot and gluteal fibrosis after intramuscular injections.
Extrapelvic compression of the sciatic nerve. An unusual cause of pain about the hip: report of five cases.
Sciatic Nerve Resection. Is That Truly an Indication for Amputation?
Sciatic Nerve Release Following Fracture or Reconstructive Surgery of the Acetabulum