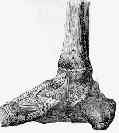
- Discussion:
- in absence of a medial malleolar fracture deltoid ligament may be stretched or torn in all oblique frx of fibula;
- this ligament prevents posterior tibial tendon from slipping into ankle joint;
- ligament ultimately heals in a lengthen position;
- these patients are often diagnosed as having chronic deltoid sprains;
- main problem, however, is lateral talar shift resulting from malunited frx of lateral malleolus or a syndesmotic ligament injury, which
widens mortise & produces chronic ankle instability;
- management of deltoid ligament injuries in association w/ fractures of the lateral malleolus is controversial;
- both operative and non operative treatment is possible;
- because talus follows fibula when deltoid is ruptured, anatomic restoration of fibula and talus restores medial anatomy & allows medial ligamentous structures
to heal without the need for operative treatment;
- repair of deep deltoid ligament is complicated by its short length & position under the medial malleolus;
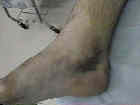
- Exam Findings:
- medial ecchymosis appears after 24 hrs when the deltoid ligament has been disrupted);
- ref: Does medial tenderness predict deep deltoid ligament incompetence in supination-external rotation type ankle fractures?
- Operative Indications:
- exploration of medial side of the ankle should be limited to cases in which the fibula and talus cannot be anatomically reduced:
- reduction may be blocked by interposed fibers of deltoid ligament or interposed posterior tibial tendon;
- evidence for mal-reduction includes medial clear space is widened by > 2 mm following reduction
- References:
- Deltoid Ligament Repair vs. Syndesmotic Fixation in Bimalleolar Equivalent Ankle Fractures.
- Fractures of the distal part of the fibula with associated disruption of the deltoid ligament. Treatment without repair of the deltoid ligament.
- Tibiotalar contact area. Contribution of posterior malleolus and deltoid ligament.
- Deltoid ligament integrity in lateral malleolar fractures: a comparative analysis of arthroscopic and radiographic assessments.