- Discussion:
- Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: (considerations: hemiarthroplasty vs TSA)
- Reverse arthroplasty
- Indications:
- indicated for end stage DJD or RA shoulder involvement;
- contra-indications to shoulder arthroplasty include combined rotator cuff / deltoid paralysis
and recent joint infection;
- in these rare circumstances, arthrodesis may be considered;
- may occur as a consequence of recurrent shoulder instability;
- infection control
- references:
- Shoulder Arthroplasty in Patients with a Prior Anterior Shoulder Dislocation. Results of a Multicenter Study.
- Dislocation arthropathy of the shoulder

- Exam:
- note the degree both preoperatively and postoperatively of scapulothoracic to glenohumeral motion;
- as noted by Friedman RJ (1997), patients with DJD of the shoulder reverse the normal 1:2 ratio of
scapulothoracic to glenohumeral motion ratio (this is not changed w/ arthroplasty);
- excessive external rotation:
- may indicated deficiency of subscapularis
- restricted external rotation:
- may indicated severe wear of the posterior glenoid, in which case the glenoid may have to be
reamed to a more neutral version;
- reference
- Prospective analysis of total shoulder arthroplasty biomechanics.
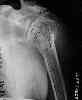
- Radiographs:
- AP radiograph in internal and external rotation
- axillary view to assess glenoid deficiencies;
- even if glenoid appears normal on the axillary view, any posterior subluxation may indicate excessive
poserior glenoid wear;
- CT scan:
- may allow better assesment of the glenoid version and possible posterior glenoid erosion;
- ref: The use of computerized tomography in the measurement of glenoid version.
- osteoarthritic changes:
- prominent osteophyte at the inferior margin of the humeral head or glenoid is characteristic;
- mild arthrosis: inferior osteophyte less than 3 mm in length;
- moderate arthrosis: inferior osteophyte between 3-5 mm in length, irregularity of the joint line and subchondral sclerosis;
- severe arthrosis: inferior osteophyte measuring more than 5 mm or if there is joint incongruity;
 - Surgical Technique:
- Surgical Technique:
- anterior approach to shoulder
- hemiarthroplasty - preparation and insertion of hemiarthroplasty
- total shoulder arthroplasty:
- glenoid component:
- total shoulder arthroplasty - video
- technical considerations with fracture
- reverse arthroplasty
- Post Operative Rehab:
- immediate begin an active assisted range-of-motion program emphasizing forward elevation and external rotation to the side;
- active strengthening should not begin for 6 weeks postoperatively to allow the subscapularis tendon repair time to heal;
- reference:
- Rehabilitation after total shoulder arthroplasty.
- Is a formal physical therapy program necessary after total shoulder arthroplasty for osteoarthritis?
- Complications of Shoulder Arthroplasty