- Hematoma:
- Infection associated with hematoma formation after shoulder arthroplasty
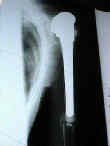
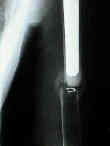
- Fractures
- fractures may occur at the tip of the prosthesis;
- long oblique and spiral fractures can be treated non operatively as long as good alignment is maintained;
- transverse or short oblique fractures may not heal with non operative treatment and operative intervention shold be consideed;
- references:
- Humeral fractures after shoulder arthroplasty.
- Humeral fracture following shoulder arthroplasty.
- Loss of Tuberosity Fixation:
- when the lesser and greater tuberosity fragments have been quatered (as is necessarily in 4 part frx), it is essential that a secure repair be re-established;
- when fixation fails, only a poor postoperative result can be expected;
- Instability:
- instability following shoulder arthroplasty should be divided into early and late;
- early dislocations:
- dislocations which occur in early post op period may be due to malposition of implant, soft tissue imbalance or due to inadequate postop protection;
- treatment involves reduction (if possible) and immobilization;
- late dislocation:
- consider rotator cuff tear, component loosenig, or glenoid wear;
- superior instability:
- most often due to supraspinatus/infraspinatus tear;
- inferior instability:
- this is avoided by noting whether the deltoid, superior cuff and capsule are adequately tensioned w/ the arm at the side;
- in some cases, unexpected inferior subluxation will be seen postoperatively;
- this may be due to loss of deltoid muscle tone, and once deltoid strength is re-established, the subluxation may improve;
- anterior instability:
- deficiency/tear of the subscapularis;
- most common reason for instability;
- anterior instability may result from avulsion of the tendon from the repair site;
- "over-stuffing the shoulder" with placement of a glenoid component will lateralize the humeral component and will place subscapularis tendon under increased tension and risk rupture;
- when diagnosed early may be amenable to surgical repair (consider Achilles tendon allograft for augmentation);
- failure to restore proper length (= proper deltoid tension);
- correct amount of retroversion (normally 30-35 mm);
- malrotation of the humeral component: retroversion less than 20 deg may lead to anterior dislocation;
- previous anterior acromioplasty and excision of the CA ligament: may allow antero-superior dislocation;
- may result from previous contracture of the posterior capsule;
- anterior deltoid dysfunction;
- posterior instability:
- may occur when the humeral component is placed in more than 45 deg of retroversion;
- may occur from posterior glenoid erosion;
- may occur from over-tightening the anterior capsule and subscapularis;
- references:
- Instability of the shoulder after arthroplasty.
- Complications of total shoulder arthroplasty.
- Complications of total shoulder-replacement arthroplasty.
- Instability After Shoulder Arthroplasty: Results of Surgical Treatment.
- Shoulder Stiffness:
- soft tissue release: subscapularis adhessions require circumferential release
- over stuffed replacement:
- consider modular downsizing of the components (reduction of humeral head diameter and offset)
- arthroscopic release:
- references:
- Long head of the biceps pathology as a cause of anterior shoulder pain after shoulder arthroplasty.
- Arthroscopic capsular release after hemiarthroplasty of the shoulder for fracture: a new treatment paradigm.
- The role of arthroscopy for the problem shoulder arthroplasty.
- Glenoid Loosening:
- Radiographic and Computed Tomography Analysis of Cemented Pegged Polyethylene Glenoid Components in Total Shoulder Replacement.
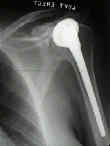
Complications of total shoulder arthroplasty: Are they fewer or different?
Rotator cuff repair after shoulder replacement.
The complex characteristics of 282 unsatisfactory shoulder arthroplasties
The outcome of resection shoulder arthroplasty for recalcitrant shoulder infections.