- See: Posterior Approach to the Humerus;
- Discussion:
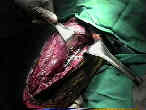
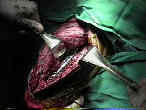
- considered to be the most versatile approach to the elbow;
- most surgeons use straight longitudinal incision, which avoids olecranon tip, by shifting the incision slightly laterally or medially;
- Variations of Posterior Approach:
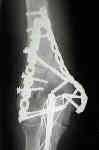
- Transolecranon Osteotomy
- indicated for condylar fractures;
- can be intra-articular or extra-articular;
- affords best visualization, of the distal articular fragments;
- Triceps Splitting: (Urbaniak)
- Tricpers Reflecting:
- Caputo Technique:
- indicated for extra-articular adult supracondylar fractures;
- uses a standard posterior skin incision;
- medial and lateral windows are created on either side of the triceps muscle;
- medially, the ulnar nerve is carefully identified from its entrance between the two heads of the FCU up to a point cephalad to the arcade of Struthers;
- see: anatomy of the cubital tunnel;
- note that dissection proximal to the arcade of Struthers may injure the brachial artery;
- laterally, the radial nerve is identified as it passes between the triceps and brachialis;
- the nerve can be found crossing this interval at a point just distal to the deltoid insertion;
- once both nerves have been identified and protected, the medial and lateral borders of triceps is identified are dissected down to bone;
- triceps can then be mobilized to either side to allow exposure to the medial and lateral sides of the distal humerus;
- Modified Pediatric Approach:
- posterior approach may be indicated for irreducible supracondylar frx (see open reduction) or for displaced lateral condyle frx;
- posterior incision is made which curves along the medial side of olecranon;
- ulnar nerve is identified and protected;
- triceps tendon is transected 1 cm from its insertion (so that an adequate cuff of tendon is left for closure);
- remaining triceps insertion is elevated medially or laterally;
- the proximal portion of the tendon is mobilized proximally;
- posterior capsule is opened transversely from medial to lateral;
- the frx site is exposed and fixed appropriately;
- triceps tendon is closed securely w/ non absorbable sutures;
- arm is then immobilized in a cast (3 weeks for supracondyalr frx and 4-5 weeks for lateral condyle frx)
The posterior approach to the elbow revisited.
The midline posterior elbow incision. An antomical appraisal.
Outcomes Following Distal Humeral Fracture Fixation with an Extensor Mechanism-On Approach