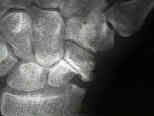
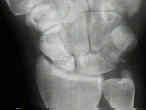
- See: Avascular Necrosis of the Scaphoid
- Discussion:
- often result from undiagnosed or undertreated non displaced scaphoid fractures, especially when associated w/ carpal instability;
- even when found as late as 6 mo after the injury, frx of scaphoid, esp at the waist and distal location, may go on to heal;
- progressive collapse & deformity usually occur at frx site, leading to subluxation of midcarpal joint and dorsal rotation of lunate;
- nature history often leads to late radioscaphoid degenerative changes, followed by pancarpal arthritis (SLAC);
- in the study by Schuind F, et al (1999), several negative factors were identified for healing;
- negative factors include use of a dorsal approach (wrist stiffness), and time lapse of more than 5 years from injury;
- authors raise the question of whether asymptomatic scaphoid non unions should undergo sugery, especially if a proximal
pole frx is present;
- ref: Prognostic factors in the treatment of carpal scaphoid nonunions.
- poor prognostic signs:
- there is concern with a capitolunate angle of > 10 deg, almost certain problem when angle is > 20 deg;
- saggital CT may pick up the deformity;
- DISI deformity, radiocarpal degenerative changes, and poor scaphoid bone quality are all poor prognostic signs;
- references:
- The natural history of scaphoid non-union.
- The natural history of scaphoid non-union. A review of fifty-two cases.
- Exam Findings:
- pts demonstrate marked loss of wrist dorsiflexion, which can be improved if the deformity is corrected;
- Radiographs:
- radiographs (including CT scan and MRI) allow determination of carpal collapse, scaphoid collapse, bone loss, and osteonecrosis;
- there is a tendency for the fracture to gap open dorsally;
- ulnar deviation opens gap radially, and extension of waist is not particularly in closing the dorsal gap;
- in some cases, it will be difficult to tell if scaphoid healing has taken place;
- a magnifying glass may reveal some trabeculation across the persistent frx radiolucency;
- if the diagnosis remains in doubt, order a CT scan w/ reformated images;
- note that a humpback scaphoid deformity is often associated w/ DISI
- upto 35% of patients demonstrate a humback deformity and about 40% demonstrate a DISI deformity;
- Nonunion of Proximal Pole:
- Early Surgical Treatment:
- in early cases, it may be possible to restore full length to scaphoid by means of bone grafting & thus correct carpal deformity;
- debridment:
- all fibrous tissue needs to be excised and replaced w/ sufficient bone graft to maintain length of scaphoid under compression;
- in cases of non-union use curets or highspeed burr to debride the non union site of fibrous tissue, while taking care not to
damage the outer cortical shell;
- it is important that the dorsal scaphoid cortex is preserved to serve as a tension band;
- reduction:
- consider using dental picks to manipulate the frx fragments into reduction;
- K wires are inserted perpendicular to frx fragments inorder to "joystick" them into reduction, but this may cause
further comminution;
- in cases of scaphoid humback deformity the lunate should be reduced before correcting the scaphoid deformity;
- the lunate should be reduced back to a neutral position by pinning it to the radius;
- cautions:
- when frxed, proximal pole tends to extend w/ lunate, & distal pole tends to flex (may result in dorsal gaping);
- osteonecrosis: consider need for vascularized bone graft;
- bone grafting:
- bone graft harvest techniques:
- Russe Bone Graft Technique:
- w/ a well alinged non union, bone graft may consist of cancellous chips;
- w/ a malaligned non union which requires reduction, bone graft should be a cortico-cancellous piece that is shaped to
fill defect;
- ref: Complications With the Use of BMP-2 in Scaphoid Nonunion Surgery
- fixation methods:
- Herbert Screw Fixation
- 3.5 mm Cannulated Screw Insertion:
- Stabilization of scaphoid type B2 fractures with one or two headless compression screws.
- Treatment of scaphoid nonunion by one, two headless compression screws or plate w/ or w/o additional extracorporeal
- Late Treatment:
- in late cases, associated soft-tissue contracture prevents complete correction but dorsiflexion usually can be improved by
lengthening the scaphoid;
- if secondary radiocarpal arthritis has occurred, limited radial styloidectomy is a useful adjunct to reconstruction;
- it relieves both pain & restriction of movement assoc w/ impingement of the scaphoid on the radius;
- Salvage Procedures:
- Four Corner Fusion;
- Proximal Row Carpectomy;
- Wrist Arthrodesis;
- limited fusion: (proximal scaphoid pole, lunate, capitate);
- motivation for this form treatment is based on the observation that the proximal pole-distal radius articulation is often spared
degenerative changes for the first decade following injury;
- indicated for chronic scaphoid non unions w/ degenerative changes, and DISI deformity (may also be used for SLD);
- may be relatively contra-indicated w/ very proximal scaphoid nonunions;
- longitudinal incision is made over the ulnar aspect of the 4th compartment;
- extensor retinaculum is incised in a step cut pattern;
- longitudinal incision is made in the wrist capsule extending to the mid carpal row;
- the distal fragmenlink.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00402-018-3087-6t is then carefull excised;
- cartilagenous surfaces between the proximal pole, lunate, and capitate are removed;
- DISI deformity of the lunate should be corrected;
- percutaneous pins are inserted: captiolunate, scapholunate, and scaphocapitate;
- cancellous bone graft is applied between the carpi;
- references:
- Limited Arthrodesis for Scaphoid Nonunion
- Scaphocapitolunate arthrodesis.
- STT fusion:
- is usually combined w/ a bone graft can be offered
Modified Murray Technique for Carpal Navicular Nonunion
Dorsal approach to scaphoid nonunion.
Percutaneous pinning of symptomatic scaphoid nonunions.
Scapholunate gap with scaphoid nonunion.
Compression-Staple Fixation for Fractures, Non-Unions, and Delayed Unions of the Carpal Scaphoid.
Treatment of ununited fractures of the scaphoid by iliac bone grafts and Kirschner-wire fixation.
Limited triscaphoid intercarpal arthrodesis for rotatory subluxation of the scaphoid.
Prognostic factors in the treatment of carpal scaphoid non unions.
Operative management of pediatric scaphoid fracture nonunion.