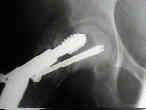
- See: Avascular Necrosis following Femoral Neck Fracture
- Discussion:
- usually non unions are apparent w/in one year of femoral neck frx;
- incidence ranges from 10 to 30%;
- only 1/3 of pts w/ AVN will require additional surgery where as
- 3/4 patients with non union will require reoperation;
- non-union is initially suspected when there is pain in groin or buttock, esp on extension of the hip or with weight-bearing;
- these symptoms occur earlier and are more severe than those from AVN;
- assessment of risk of non-union:
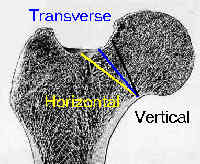
- in the study by Hammer, the author assessed risk of non union using modified Pauwel's radiographic classification;
- modified Pauwel's method classifies frx as horizontal, transverse, or vertical, according to the direction of the fracture on the femoral head;
- 11/11 Garden II frx w/ horizontal frx line had non-union;
- 2/5 Garden II frx w/ vertical frx line had non-union;
- 6/14 Garden III frx w/ vertical frx line had non-union;
- 2/5 Garden IV frx w/ vertical frx line had non union;
- references:
- Nonunion of subcapital femoral neck fractures.
- Avascular necrosis and nonunion after osteosynthesis of femoral neck fractures: effect of fracture displacement and time to surgery.
- The vertical hip fracture - a treatment challenge. A cohort study with an up to 9 year follow-up of 137 consecutive hips treated with sliding hip screw and antirotation screw.
- Radiographs:
- show a radiolucent zone, and tomography confirms the lack of healing;
- look for:
- change in fracture position by 10 mm;
- change in screw position by 5%
- backing out of the screws
- perforation of the femoral head
- as in this case, there will often be hardware failure or cut out of nail;

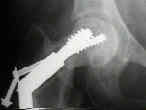

- Bone Scan:
- shows high uptake will be seen in area of non-union;
- MRI:
- non-union may be accompanied by osteonecrosis;
- MRI may be used to evaluate viability of femoral head before the options for treatment are considered;
- Labs:
- CBC, sed rate, and CRP inorder to help rule out infection;
- Management: Young Patients:
- in younger pt refixation w/ cancellous graft & valgus osteotomy may be indicated;
- in most non unions there is a vertical fracture line (causing shear stress rather than compression across the frx site) and most non-unions have drifted into some varus angulation;
- valgus intertrochanteric osteotomy
- makes fracture line more horizontal and converts shear forces at nonunion site to compressive forces, which then promote fracture healing;
- references:
- Intertrochanteric osteotomy for non-union of the femoral neck.
- Intertrochanteric osteotomy using a dynamic hip screw for femoral neck nonunion.
- Valgus intertrochanteric osteotomy for malunion and nonunion of trochanteric fractures.
- Valgus intertrochanteric osteotomy for neglected femoral neck fractures in young adults.
- in younger pt who has collapse of femoral head concurrent w/ non-union, total hip replacement is indicated;
- references:
- Ununited femoral neck fractures by open reduction and vascularized iliac bone graft.
- [Valgus osteotomy in the treatment of pseudoarthrosis of the femoral neck: 41 cases]
- Femoral neck nonunion treatment
- Triple attack technique for non-union of femoral neck fractures
- Management of Elderly Patient:
- in elderly pt who is able to walk about the community, a non-union is treated with a total hip replacement;
- references:
- Long-term results of total hip arthroplasty for femoral neck fracture nonunion.
Ununited femoral neck fractures by open reduction and vascularized iliac bone graft.
Femoral neck nonunion treatment
The treatment of nonunion after intracapsular fracture of the proximal femur.
Valgus osteotomy for delayed presentation of femoral neck fractures Pauwels Grade III.

