- Discussion:
- at time of the injury, calcaneus is driven up toward center of body;
- lateral wall is driven outward, as are the peroneal tendons;
- this results in shortened functional length of gastrocnemius-soleus complex, flat foot, lateral impingement of peroneal structures, & locked transverse tarsal joint;
- when pt stands, position of talus is relatively dorsiflexed due to impaction of posterior facet of the calcaneus;
- this results in limited ability to dorsiflex foot and, at times, to achieve tibiotalar impingement;
- most important, sub-talar joint is often incongruous & painful;
- Complications:
- Wound Healing Complications:
- in the study by Sanders, et al, the authors reported 8 wound dehiscences, 3 below-knee amputations, and 5 free tissue flaps because of wound complications in 120 fractures;
- in the report by Shuler FD, et al, the authors report that restoration of calcaneal height and length (in severely comminuted fractures) may have the effect of increasing wound tension and thus has the effect of increasing wound complications;
- references:
- Operative treatment in 120 displaced intraarticular calcaneal fractures. Results using a prognostic computed tomography scan classification.
- Wound-healing risk factors after open reduction and internal fixation of calcaneal fractures: does correction of Bohler's angle alter outcomes?
- Calcaneal Widening
- Varus and Valgus Deformities:
- malposition is seen after both operative and nonoperative treatment;
- most common deformity is residual varus angulation of the hindfoot which occurs as a result of incomplete reduction of the tuberosity;
- clinical varus is best seen when patient raises up on the toes;
- Heel pain resulting from rupture of fibrofatty septa w/in heel pad;
- Subtalar Joint Arthritis:
- see subtalar joint
- pain on wt bearing, & pain aggravated by inversion and eversion of foot;
- source of pain can frequently be identified by injection of lidocaine into joint, thru sinus tarsi, using x-ray control if necessary;
- source of pain can also be identified w/ differential injections & w/ use of short leg walking cast for 2 to 3 weeks;
- radiographs:
- talacalcaneal angle (lateral view) is measured from the talar axis line and calcaneal axis lines;
- heel height is measured from the talar dome to the base of the calcaneus;
- subtalar fusion;
- subtalar bone block fusion method (Carr et al 1989) attempts to restore the relationships of the tibiotalar and subtalar joints by relieving the anterior and lateral impingement and lessen shoewear difficulties;
- a lamina spreader may be placed into the subtalar joint (for distraction and exposure), but it is important to place the lamina spreader as medially as possible so as to avoid varus positioning of the subtalar joint;
- because the subtalar anatomy has been disrupted, it is essential that the surgeon be sure that there are no "islands" of intact posterior facet which are hidden by scar tissue;
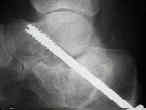
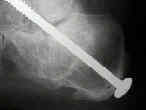
- in the following example, the surgeon neglected to remove a significant portion of the posterior facet, and the result was a subtalar nonunion; (note the "windshield wiper" effect near the screw head)
- often the lateral wall needs to be removed to relieve any residual calcaneal-fibular abutment;
- a tricortical graft (from iliac crest) is placed in the subtalar interval inorder to restore heel height;
- be sure that the heel is in the proper amount of valgus during this portion of the case;
- use flouroscopy to help guide two 6.5 mm screws from the posterior heel into the talar neck;
- references:
- Late results of subtalar distraction fusion.
- Subtalar distraction bone block fusion for late complications of os calcis fractures.
- Lateral talocalcaneal angle in assessment of subtalar valgus: follow up of seventy Grice Green arthrodeses.
- Peroneal Tendinitis:
- impact of fracture compresses tendons against the fibula as calcaneus widens and displaces laterally;
- pain may be from dislocation of tendons or from impingement of tendons on tip of fibula from widened calcaneus;
- relief of pain following injection of peroneal tendon sheath w/ local anesthetic gent may confirm the diagnosis;
- peroneal tenogram may also confirm dx by demonstrating impingement;
- treatment involves excision of excessive bone of the lateral calcaneus sural nerve decompression, & rerouting of tendons behind malleolus;
- alternatively consider resection of the tip of the lateral malleolus;
- Calcaneofibular Abutment;
- ref: Calcaneo-fibular abutment following crush fracture of the calcaneus.
- Tibio-talar Impingement (horizontal talus):
- among deformities that can occur following calcaneus frx is horizontal talus;
- this causes tibiotalar neck impingement, loss of dorsiflexion, & ankle pain;
- pts will have pain when walking uphill
Late complications of fractures of the calcaneus.
Subtalar distraction bone block fusion for late complications of os calcis fractures.