- See:
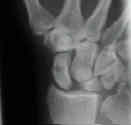
- PA View
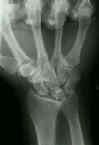
- AP View
- Radiology of Hand & Wrist
- Radiology of Scaphoid Fracture
- Discussion:
- clenched fist AP - ulnar deviation view (see: AP view:)
- proper technique: for visualizing scapholunate interval;
- gap is more noticeable on AP view that is made w/ wrist supinated than it is on more usual PA view (made w/ wrist pronated);
- direct x-ray beam parallel to scapholunate joint;
- specific findings:
- scapholunate interval > 2-3 mm as compared to the opposite side (Terry Thomas sign);
- if the diagnosis is in doubt, compared the scapholunate interval to the luno-triquetral internval;
- a true S-L diastasis will show a significant widening of the SL interval vs the LT interval;
- cortical ring sign:
- produced by cortex of distal pole of palmar flexed scaphoid;
- produced by cortical outline of the distal pole of scaphoid;
- scaphoid is foreshortened;
- distance between scaphoid ring & proximal pole is < 7 mm;
- negative ulnar variance:
- axial scaphoid shift sign:
- normally a smooth arc can be outlined around the scaphoid, lunate, and the triquetrum;
- w/ scapholunate injury, the arc will be broken as the scaphoid migrates proximally;
- this finding may be useful in the presence of scapholunate injury which occurs in the presence of a distal radius fracture;
- misc:
- ulnar deviation, increases scapholunate gap;
- radial deviation, closes gap;
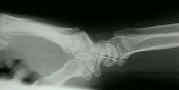
- Lateral view:
- scapholunate angle formed by intersection of longitudinal axes of scaphoid & lunate avg 46-47 deg & ranges from 30-60 deg;
- in SLD, scaphoid is palmar-flexed w/ prox migration of capitate;
- angle > 60-70 deg suggests SLD;
- capitolunate angle of > 15-20 deg is strongly suggestive of SLD;
- normally it should be possible to draw straight line thru longitudinal axis of radius, lunate, & capitate;
- in SLD lunate and triquetrum are displaced ulnarly;
- when lunate lies plamar to capitate but faces dorsally, collapse pattern is referred to as DISI;
- Wrist Arthrography
- MRI:
- in general MRI has poor sensitivity for the diagnosis of SLD (less than 40%);
- in the study by Schädel-Höpfner M, et al, in a prospective study 103 patients with clinically or radiologically suspected tears of the scapholunate interosseous ligament were investigated with MRI and wrist arthroscopy;
- MRI was performed with the conventional technique in 72 cases and after intravenous injection of contrast medium in the remaining 31 patients;
- correct diagnosis was made by MRI in 75% of cases and its overall sensitivity and specificity were 63% and 86% respectively;
- there was no statistical difference in the accuracy of MRI for acute or chronic tears and the use of IV contrast medium did not improve its accuracy;
- the authors conclude that MRI is not recommended for the diagnosis of scapholunate ligament injury;
- ref: MRI versus arthroscopy in the diagnosis of scapholunate ligament injury.
Midcarpal wrist arthrography for detection of tears of the scapholunate and lunotriquetral ligaments.
Is this scapholunate joint and its ligament abnormal?
Demonstration of the scapholunate space with radiography.
Obvious radiographic scapholunate dissociation: X-ray the other wrist.