 - See:
- See: - Carpal Instability:
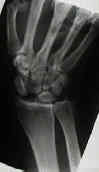
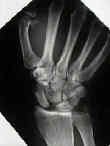
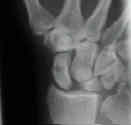
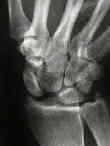
- scapholunate advanced collapse
- scapholunate instability
- Discussion:
- scapholunate and lunate injuries cause tenderness just distal to Lister's tubercle;
- marked prominence of the entire carpus dorsally may indicate of a perilunate dislocation;
- SLD is characterized by limited range of motion and increased weakness;
- Watson test:
- this test provokes dorsal subluxation of the proximal scaphoid over the dorsal rim of the radius, as the wrist is radially deviated;
- is performed by grasping the patient's hand from its ulnar aspect of the small metacarpal with the examiner's thumb on the palmar surface of the distal pole of the scaphoid;
- alternatively, the patient's hand is grasped by the examiner's hand from the radial aspect of the index metacarpal with the thumb and the palmar surface;
- it is critical for the examiner's thumb to apply pressure to the distal pole of the scaphoid, in order to prevent it from flexing;
- move wrist from ulnar to radial deviation w/ distal tuberosity compressed;
- as scaphoid flexes to more vertical orientation w/ radial deviation, tuberosity compression forces proximal pole subluxation dorsal to lip of radius;
- as the examiner's thumb pressure is removed, the subluxed scaphoid reduces, and may produce a palpable clunk and dorsal wrist pain (indicating instability of the scapholunate ligament);
- this test has been criticized for low specificity;
- in the study by Wolfe, et al (1997), 36% of normal individuals had a positive shift test;
- when examined flouroscopically, many of these individuals had a capitolunate instability;
- Kinematics of the scaphoid shift test.
The scaphoid shift test.