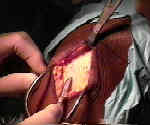
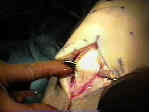
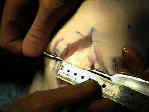
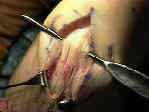
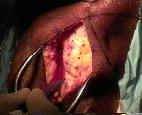
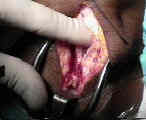
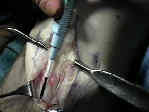
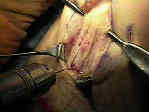
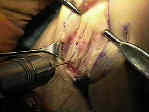
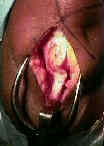
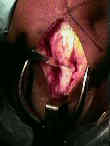
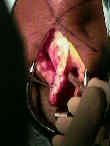
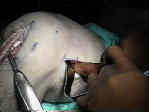
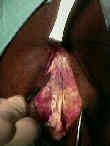
- Skin Incision:
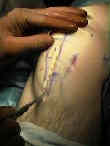
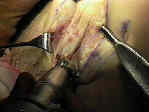
- 5-7 cm incision is made from inferior patellar pole to a point just medial to the tibial tubercle;
- incision is taken down thru skin and subcutaneous tissues using scalpel;
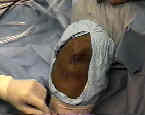
- Incising the Patellar Tendon:
- limb was exsanguinated & tourniquet is inflated.
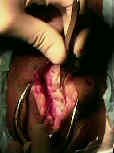
- joker may be inserted underneath patellar tendon & moved both proximally and distally;
- 10 mm of approx 30 mm tendon is then incised after patella is gently dissected from the fat pad;
- use the back end of the knife to split the tendon;
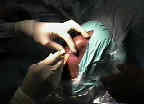
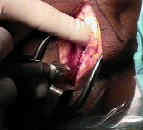
- Outline Bone Plugs:
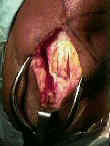
- out line 1 inch long patellar and tibial bone plugs;
- drill two 2 mm holes in the outlined tibial and patellar bone plugs;
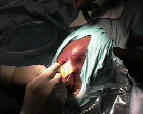
- Saw Out Tibial Bone Plugs:
- 2.5 cm of bone plug are taken both proximally & distally using bone saw;
- first complete the tibial tubercle harvest;
- bone saw is held at 45 deg angles and completed w/ 1/4 inch curved osteotome
- do not pry the osteotome, but rather wiggle it from side to side;
- #2 Tycron is placed thru drill holes;
 ***
*** 
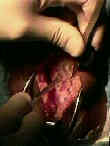
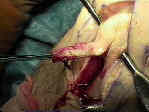
- Patellar Bone Harvest:

- grab the tibial bone plug over a lap sponge and pull it distally which allows better exposure of the patellar bone plug;
- complete the patellar plug harvest:
- 2 drill holes are made in the outlined patellar graft and then harvest w/ saw;
- Patellar Tendon Graft Preparation:
- Donor Site Healing:
- as noted by Proctor et al 1997 in an experimental goat study, the patellar tendon defect fills in with collagenous
scar tissue that was less organized, more cellular, and more vascular than seen in the normal ACL;
- in addition the scar tissue had an increased cross sectional area (increased by 42%) but had only approximately half the maximum
force to failure;
- bone plug harvest sites were not bone grafted and did not fill in this study;
- conclusion: the scar tissue which replaces the graft defect is unsuitable for revision ACL;
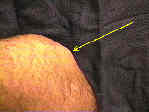
- case example:
- this 33 year old orthopaedic surgeon underewent a bone-patella-bone ACL reconstruction and developed
a painful exostosis over the patella harvest site;
- as a result, he was unable to knee down on the ground;
Reconstitution of the patellar tendon donor site after graft harvest.
Isolated autogenous bone-patellar tendon-bone graft site morbidity.