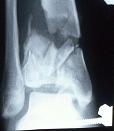
- Classification: (Ruedi-Allgower):
- type I: pilon Frx
- malleolar frx w/ significant axial load at time of injury & therefore large posterior plafond fragments;
- type II: pilon Frx
- spiral extension frx;
- type III: pilon Frx
- type III frxs are central compression injuries w/ impaction of talus into distal tibia w/ or w/o concomitant fibular frx;
- subdivided as discussed into subgroups A-C depending on degree of displacement of articular surface & presence or
absence of comminution and/or impaction;
- type A:
- minimal or no anterior tibial cortical communition, > 2 large tibial articular fragments, and usually a fibular fracture of transverse
or short oblique at the level of the plafond (or ankle joint);
- type B:
- results from severe axial compression force, causing distal tibial bony impaction and comminution
___________________________________________________________________________________________________
OA for the Study of Internal Fixation and AOrthopaedic Trauma Association Classification
Type A: Distal tibial metaphyseal injuries without intra-articular extension
A1: Simple
A2: Comminuted
A3: Severely comminuted
Type B: Partial articular fractures
B1: Pure split
B2: Split with depression
B3: Depression with multiple fragments
Type C: Fracture involves the entire joint surface
C1: Simple split in the articular surface and the metaphysis
C2: Articular split that is simple with a metaphysis split that is multifragmentary
C3: Fracture with multiple fragments of the articular surface and the metaphysis

