 - See posterior tibial artery
- See posterior tibial artery
- Anatomy:
- anterior tibial artery passes from behind through gap above interosseous membrane to enter anterior compartment of leg and supply its muscles;
- as it crosses membrane, it gives off a recurrent branch;
- ref: The risk of injury to anterior tibial artery in posterolateral approach to the tibia plateau: A cadaver study.
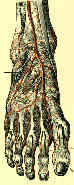
- it continues on dorsum of foot as dorsalis pedis artery, which gives off medial and lateral tarsal branches;
- ends by dividing into arcuate artery and the larger deep plantar artery;
- arcuate artery has three metatarsal branches that, in turn, divide into dorsal digital arteries;
- deep plantar artery sends digital branches to great toe and second toe and passes between heads of the first dorsal interosseous muscle to the plantar surface;
- Exposure:
- anterior tibial artery is exposed thru a longitudinal incision in lateral calf over the mid portion of anterior compartment;
- dense fascia of the anterior compartment is incised and dissection deepened between the bellies of the long extensors;
- tibialis anterior and EHL muscle bodies are frequently fused, and neurovascular bundle is usually exposed between these and the extensor digitorum muscle;
- here artery, its paired tibial veins, and the tibial nerve lie along surface of the interosseous membrane;
- presence of a dorsalis pedis pulse does not rule out injury to A.T.A., since there may be retrograde blood flow from posterior tibial artery
Prevalence and surgical significance of a high-origin anterior tibial artery.
Arterial injury complicating knee disruption. Third place winner: Conrad Jobst award.
Successful management of trifurcation injuries.
Optimal management of tibial arterial trauma.
Optimal management of tibial arterial trauma.
Traumatic popliteal and trifurcation vascular injuries: determinants of functional limb salvage.
Microarterial anatomy of the lesser toe proximal interphalangeal joints.

