- See: Spondyloepiphyseal Dysplasia Tarda:
- Discussion:
- a type of short trunk disproportionate dwarfism, in which there is involvement of the vertebra and epiphyseal centers;
- can be transmitted as autosomal dominant trait, although most cases arise as random mutations;
- symptoms include delayed developmental milestones, diminished endurance, and respiratory dysfunction;
- children may appear hypotonic;
- these patients are predisposed to premature DJD;
- type II collagen defects are found in spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia
- Diff Dx:
- Morquio's Syndrome:
- x-ray manifestations of Morquio's disease include wide flaring of ilium, no delay in pubic ossification, shallow acetabula, coxa
valga, and severe involvement of hands and feet;
- achondroplasia:
- other forms of spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia:
- chondrodysplasia punctata
- spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia tarda
- Eyes:
- eyes are wide set;
- retinal detachment & severe myopia may occur in > 50% of cases;
- Hands:
- hands and feet are relatively normal in length, in striking contrast to extreme shortnesss of proximal
and middle segments of limbs;
- Hip and Knee:
- coxa vara
- almost universal in varying degrees of severity;
- develops early and may result in discontinuity of the femoral neck.
- valgus intertroch osteotomy is indicated for varus deformity of 100 deg or less, progressive varus, high-grade
epiphyseal angle, & presence of unossified triangular metaphyseal frag in femoral neck;
- get preop arthrography to determine most congruent alignment;
- ossification of capital femoral epiphysis is delayed & often does not appear until age 5 years;
- combination of delayed ossification, high riding femur, and limited abduction often gives the false impression of a dislocated hip;
- progressive subluxation can occur & may result in precocious arthritis;
- genu valgum is usually present;
- Cervical Spine:
- atlantoaxial instability:
- may occur due to odontoid hypoplasia or os odontoideum;
- may result in cervical myelopathy;
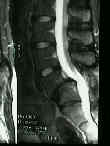
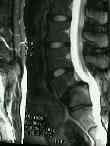
- Spine:
- involvement of vertebrae and epiphyseal centers results in a short trunk disproportionate dwarfism;
- lateral radiograph may reveal small misshapen vertebral bodies with a mild thoracolumbar kyphosis;
- progressive kyphoscoliosis may develop in late childhood;
- treated as indicated w/ bracing or posterior instrumentation and fusion;
- lumbar lordosis is usually secondary to hip flexion contractures;
- Feet: talipes equinovarus is common
Genetic heterogeneity in spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia congenita.

