- Harris Beath View
- Oblique View:
- patient is supine with the knee flexed;
- lateral border of the foot is elevated 40 to 45 degrees with
- medial border of the foot against the cassette;
- central beam is directed vertically to the base of the 3rd M.T.
- Broden's View
- Sesamoid View:
- used to obtain a tangential view of the sesamoid bones of MT heads
- pt is seated on the table with the foot dorsiflexed on cassette;
- toes are held in a dorsiflexed position with a strip of gauze;
- central beam directed vertically to the head of the 1st M.T.
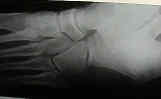
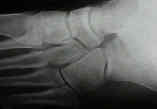
- Oblique View:
- patient is supine with the knee flexed;
- lateral border of the foot is elevated 40 to 45 degrees with
- medial border of the foot against the cassette;
- central beam is directed vertically to the base of the 3rd M.T.
- Broden's View
- Sesamoid View:
- used to obtain a tangential view of the sesamoid bones of MT heads
- pt is seated on the table with the foot dorsiflexed on cassette;
- toes are held in a dorsiflexed position with a strip of gauze;
- central beam directed vertically to the head of the 1st M.T.

- Radiographic Relationships:
- talo-calcaneal angle:
- draw lines thru the long axis of the talus and the calcaneus
- normal range = 20 to 40
- talo first metatarsal angle
- draw lines thru the long axis of the talus & 1st metatarsal
- normal range = 0 to - 20 deg

