- See:
- Total Hip Replacement Menu:
- Acetabular Bone Grafting:
- Allografts
- Discussion:
- indicated for pts w/ severe osteolysis or for femoral shaft fractures;
- in younger pts, structural allografting may eventually allow some degree of revascularization of dead bone, which restores patients bone stock;
- napkin ring calcar replacement:
- involves placement of a circumferential portion of allograft over top of the patients deficient calcar;
- femoral component is then inserted in the usual way (usually w/ cement);
- main complications include graft resorption and subsidence;
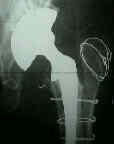
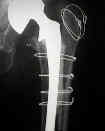
- femoral strut allografts:
- in the report by Barden B, et al. (2001), large femoral cortical strut allografts were used to provide structural
support of the femur in 20 patients in whom uncemented, extensively porous-coated, press-fit revision femoral stems;
- mean followup was 4.7 years;
- radiographic analysis of the patients who had revision surgery revealed that in all 20 patients, cortical femoral strut allografts showed incorporation;
- small areas of graft resorption were observed in only two patients;
- 17 of the uncemented femoral revision stems radiographically showed bone ingrowth;
- 3 of the revision femoral stems were interpreted as being fixed only by fibrous ingrowth after early subsidence after surgery;
- before surgery, all patients were unable to walk and had severe pain;
- at followup, all patients were ambulatory and had considerable improvement in pain relief and in their ability to walk;
- ref: Supportive strut grafts for diaphyseal bone defects in revision hip arthroplasty.
- Technical Pearls:
- in many cases, surgeons will elect to bridge a femoral shaft defect (or fracture) with a cortical strut allograft and cables;
- realize that with time, the allograft may undergo partial resorption which can lead to wire loosening;
- hence, cortical strut allografts and wires should not be relied upon to provided long term support
Massive allografting for severe failed total hip replacement.
Intraluminal allograft restoration of the upper femur in failed total hip arthroplasty.
Fate of bone grafts in acetabular roof reconstructions assessed by roentgenography and scintigraphy.
Osteointegration of bone graft in porous-coated total hip arthroplasty.
Proximal femoral allografts for reconstruction of bone stock in revision arthroplasty of the hip.
Proximal femoral allografts in revision total hip arthroplasty.
Freeze-dried proximal femur allografts in revision total hip arthroplasty. A preliminary report.