- Discussion:
- rupture of quadriceps tendons is most common in the 6th & 7th decades, and is probably associated w/decreased vasculature;
- Male:female 8:1
- more common w/ cortisone injections, diabetes, chronic renal failure; hyperthyroidism, and gout;
- tear may involve either portion of trilaminar tendon or its entirety;
- usually the tear is initiated centrally and progresses peripherally;
- tendon usually ruptures transversely at the osteotendinous junction;
- rupture often extends thru the vastus intermedius tendon, proximal to the rupture of the rectus femoris tendon;
- its level usually corresponds to amount of flexion at time of injury;
- superficial and deep tears rarely involve the trilaminar structure at the same level;
- unlike the achilles tendon rupture, the quadriceps disruption is usually associated w/ intense pain, although in cases of chronic tendon
atrition (as from renal failure) pain may be minimal;
- Clinical Presentation:
- large hemarthrosis
- freely mobile patella and an impressive loss of extensor function with intact knee flexion;
- patient is unable to walk;
- look for palpable defect(suprapatellar gap) swelling 2nd to hemarthrosis, pt unable to extend the knee;
- hemarthrosis/swelling may mask defect; aspiration or knee flexion may widen the gap by shortening the rectus
- quad tendon usually ruptures transversely just proximal to patella;
- partial tears
- an extensor lag usually is present;
- in these patients, MRI may delineate the extent of injury.
- partial tears of quadriceps tendon may be treated nonsurgically w/ immobilization and early range of motion.
- Radiographs: 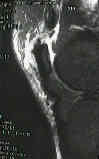
- may show patella in a lower position than normal, use contralateral patella for comparison;
- Insall-Salvati method for determining patella alta/baja
- Constant relationship length of patella (P) and length of the patellar tendon (T)
- Normal (T/P) = 0.80 - 1.2
- Patella Infera/Baja < .80 possible Quad tendon rupture
- Patella Alta > 1.2 possible Patella tendon rupture
- Surgical Treatment:
- rupture is repaired within 7 days if possible;
- early intervention allows end-to-end repair of the tendon as well as tendon to bone anchorage;
- make anterior longitudinal incision in midline of extremity;
- transossoeous repair:
- fibers of rectus femoris tendon are sutured to superior pole of patella through drill holes, as is done for
patellar tendon ruptures;
- roughen the surface of the patella to promote healing;
- take care not to place the drill holes too close to the anterior patellar surface, (in order to avoid patellar tilt);
- place drill holes in center of patella (with respect to AP), so bias the drill hole slightly toward to the articular surface;
- No 5 Ethibond/Fiberwire suture is then passed thru the quadriceps tendon (using the Krachow or Becker technique)
and then is passed thru the drill holes;
- because rupture nearly always takes place early thru an area of degeneration, consider reinforcement of
sutures w/ fascia strips;
- if the repair is strong, consider not repairing the lateral retinaculum (if it is torn) inorder to avoid patellar subluxation;
- references:
- Primary repair of quadriceps tendon ruptures. Results of treatment.
- Transpatellar refixation of acute quadriceps tendon ruptures close to the proximal patella pole using FiberWire
- A method of repair for quadriceps tendon or patellar ligament (tendon) ruptures without cast immobilization. Preliminary report.
- Scuderi technique:
- triangular tongue of tissue distally from the anterior surface of the proximal tendon;
- from anterior surface of proximal part of tendon fashion triangular flap 2-3 mm thick, 7.5 cm long on each side, and 5 cm wide;
- the base of the flap is left attached 5 cm above the rupture;
- the proximal tip of the flap is then turned over the rupture and is sutured in place;
- turn down triangular distally and suture it in place across rupture;
- Codivilla technique:
- indicated for chronic ruptures where the tendon edges cannot be opposed;
- create a full thickness inverted V flap which ends 1.5 cm above the rupture;
- the tendon edges are repaired w/ heavy suture;
- the proximal portion of the inverted V is closed down (coverting it to a verticle line);
- Post Operative Care:
- immobilize for 4-6 weeks, and then begin ROM, followed by crutch walking for 6-8 weeks
- patients passive and active flexion is limited by a hinged brace set to 30 deg. for 2 weeks, then increased to 60 deg for 2-4 weeks, and then
to 90 deg for weeks for 4-6 weeks post op;
- patiens are allowed full body weight being;
- references:
- Postoperative functional rehabilitation after repair of quadriceps tendon ruptures: a comparison of two different protocols.
- A method of repair for quadriceps tendon or patellar ligament (tendon) ruptures without cast immobilization. Preliminary report.
Bilateral simultaneous rupture of the quadriceps tendons. A report of four cases and review of the literature.
Ruptures of the extensor mechanism of the knee joint.
Outcomes following repair of quadriceps tendon ruptures.
Complications in Brief: Quadriceps and Patellar Tendon Tears.

