- Radiographic Evaluation:
- SH Type I:
- physeal frx about knee are more common than lig. injuries in children;
- stress-views & circumferential physeal tenderness help to make the diagnosis;
- SH Type II:
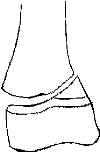
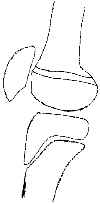
- most common frx pattern of distal femoral physis;
- growth arrest, partial or complete, w/ progressive angulation &/or shortening ranges from 30% & 80% of pts;
- look for oblique frx across one corner of adjacent metaphysis;
- displacement is usually in coronal plane w/ metaphyseal frag on side toward which the epiphysis is displaced;
- anatomic reduction can usually be obtained by closed means and maintained by percutaneous crossed K wires & spica cast
- SH III:
- look for vertical fracture line originating from intercondylar notch;
- reduction may be unstable and require internal fixation;
- SH IV:
- frx line extending from the articular surface of the epiphysis upward across physis & out through metaphysis reflecting SH IV injury;
- x-rays should be inspected carefully Thurston Holland sign
- even small metaphyseal fx indicates SH IV, rather than SH III
- SH V:
- decreased in nl width of radiolucent physis (which measures 3-5 mm until 8-10 yrs may indicate a SH type-V compression injury
- SH Type I:
- physeal frx about knee are more common than lig. injuries in children;
- stress-views & circumferential physeal tenderness help to make the diagnosis;
- SH Type II:


- most common frx pattern of distal femoral physis;
- growth arrest, partial or complete, w/ progressive angulation &/or shortening ranges from 30% & 80% of pts;
- look for oblique frx across one corner of adjacent metaphysis;
- displacement is usually in coronal plane w/ metaphyseal frag on side toward which the epiphysis is displaced;
- anatomic reduction can usually be obtained by closed means and maintained by percutaneous crossed K wires & spica cast
- SH III:
- look for vertical fracture line originating from intercondylar notch;
- reduction may be unstable and require internal fixation;
- SH IV:
- frx line extending from the articular surface of the epiphysis upward across physis & out through metaphysis reflecting SH IV injury;
- x-rays should be inspected carefully Thurston Holland sign
- even small metaphyseal fx indicates SH IV, rather than SH III
- SH V:
- decreased in nl width of radiolucent physis (which measures 3-5 mm until 8-10 yrs may indicate a SH type-V compression injury

