- See:
Total Hip Replacement Menu:
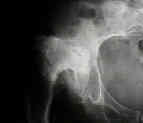
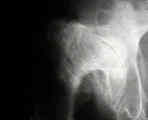
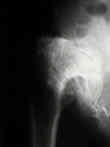
- total hip in DDH
- acetabular component menu:
- crowe classification
- Non Anatomic Positioning of the Acetabulum in DDH: (high hip center)
- advantages:
- technically easier than anatomic placement;
- surgeon can place a small uncemented cup into live host bone and avoid the need for structural autograft;
- disadvantages:
- include poor acetabular bone stock, leg length inequality a higher rate of impingement and dislocation, and higher loosening rate;
- because of illiac bone slopes upward, placement of acetabular component in the high hip center, means that there will be lateralization of hip center;
- superior and lateral positioning of acetabular component are strong predictors of acetabular loosening (and may increase femoral loosening as well);
- abduction may be limited w/ non anatomic positioning;
- impingement of the femoral neck against the ischium may occur;
- technical considerations:
- requires adequate bone stock, and leg length discrepancy less than 3 cm;
- it is important to avoid lateralization of the acetabular component;
- it is important to achieve adequate acetabular coverage (50-60 %);
- coverage is achieved by medialization down to the inner table;
- it is important to avoid reaming any more of the superior roof than is necessary;
- consider size of the acetabular components:
- ensure that small size reamers and acetabular shells are available (as small as 36 mm);
- corresponding small femoral head sizes need to be available;
- if the center of acetabulum is medialized more than 1 cm, then an increased offset femoral component should be available (to restore gluteus medius tension,
should this be a problem);
- a long neck femoral component may be necessary to restore leg lengths;
- references:
- Failure of acetabular autogenous grafts in total hip arthroplasty. Increasing incidence: a follow-up note.
- Proximal placement of the acetabular component in total hip arthroplasty. A long term follow up study.
- case example:
Femoral head autografting with total hip arthroplasty for lateral acetabular dysplasia. A 12-year experience.
Bateman bipolar hips with autologous bone graft reinforcement for dysplastic acetabula.
Arthroplasty in high congenital dislocation. 21 hips with minimum five-year follow-up.