-See: Acetabular Osteotomies
- Discussion:
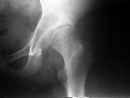
- a acetabular osteotomy salvage procedure which is indicated in patients without a concentrically reducible hip;
- modified shelf osteotomy above acetabulum w/ medial displacement of acetabulum;
- distal fragment is displaced medially and upward as osteotomy hinges on the symphysis pubis;
- hip capsule is interposed between newly formed acetabular roof & femoral head;
- relies on periarticular soft tissue metaplasia for coverage;
- femoral head is placed beneath surface of bone & joint capsule & corrects pathologic lateral displacement of the femur;
- medialization will reduce the lever arm and will reduce joint loading;
- because the biomechanics of the hip are improved by displacing hip nearer the midline, a Trendelenburg limp is often elminated;
- clinical results are mixed & are affected by patient age & degree of DJD;
- indications:
- for patients over 4 years of age;
- recommended in cases w/ inadequate femoral head coverage, w/ moderate dysplasia and moderate subluxation
- generally considered when other reconstructions are impossible;
- when femoral head cannot be centered adequately in acetabulum by abduction and internal rotation;
- symptomatic subluxated hips w/ early signs of OA;
- for dislocations that have been reduced but have later become subluxations;
- preoperative center-edge angle of at least minus 10 degrees are desirable selection criteria.
- contra-indications:
- complete obliteration of the joint space;
- labral tear:
- tear usually leads to a poor result;
- if torn labrum is found, it should be repaired or resected;
- arthrogram will rule out labral tear;
- bilateral Chiari osteotomies may be contraindicated in women because it may interfere with child rearing;
- Technique:
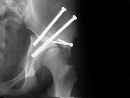
- iliac osteotomy is angled from the sciatic notch to the ASIS (anterolateral distally to posteromedial proximally);
- avoid placing iliac buttress into a horizontal position since this will cause a persistently unstable joint laterally;
- following osteotomy, a triangular osseous defect anteriorly which is stabilized w/ curved plate of bone graft from iliac wing;
- inadequate stabilization of anterior defect will result in anterior instability;
- acetabulum is displaced medially;
- acetabulum is abducted into a more vertical & medial position and replaces it w/ joint capsule supported by osseous buttress of the iliac wing;
- distal (acetabular) fragment is displaced medially and adducted;
- proximal (iliac) fragment is not allowed to move laterally;
- inferior surface of proximal fragment forms roof over femoral head;
- Case Examples:
- Post Op:
- partial weight-bearing for at least three months to allow for capsule metaplasia;
- Complications:
- this procedure will shorten the affected leg
Extra-articular augmentation for residual hip dysplasia. Radiological assessment after Chiari osteotomies and shelf procedures.
Modified Chiari pelvic osteotomy: a long-term follow-up study.
Chiari osteotomy in the treatment of congenital dislocation and subluxation of the hip.
Biomechanical analysis of the Chiari pelvic osteotomy. Preserving hip abductor strength.
Chiari pelvic osteotomy in children and young adults.
Chiari Pelvic Osteotomy for Advanced Osteoarthritis in Patients with Hip Dysplasia.