- Restoration of Length:
- may be obtained w/ use of femoral distractor or external fixator placed in distal 1/3 of the tibia and the talus or calcaneus;
- two pins are placed perpendicular to the anatomic axis and therefore parallel with the joint surfaces of the tibia;
- two additional pins are placed anterior to posterior through talus or calcaneus, and distraction is applied thru femoral distractor or
external fixation device; (see foot inclusion)
- length is obtained & joint is held apart for better visualization;
- Restoration of Articular Surface: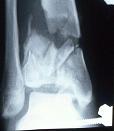
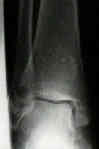
- once length is restored & articular congruity is resored, then distal tibia metaphyseal fracture is reduced along
w/ medial malleolus and temporarily held with K wires;
- anterior joint capsule is opened to inspect articular surface of talus & tibial plafond;
- generally, the articular surface is reconstructed from medial to lateral and from anterior to posterior using cannulated screws;
- screws directed in the saggital plane and directed in the coronal plane maximizes stability;
- use CT to help plan the optimal direction of cannulated screws;
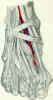
- key to articular reconstruction is lateral fragment, which should be in anatomically correct position if connected by inferior
tibiofibular ligament to already anatomically fixed fibula;
- metaphyseal reduction technique:
- small window is made superior to the frx site;
- k wire is then inserted down the medullary canal, and this wire is then used to "push" the superiorly displaced fragments down into position;
- ref: Combined percutaneous internal and external fixation of type-C tibial plafond fractures. A review of twenty-two cases.
- tillaux fragment:
- in many cases, anterolateral (Tillaux) fragment will be recognized both on x-rays and CT scan;
- retraction of this fragment will allow exposure of the wt bearing surface of the ankle joint;
- after the articular surface has be reconstructed, replacement of this fragment will help the surgeon judge length of the tibia as referenced off the tibia;
- disimpaction:
- if joint surface is superiorly displaced and impacted into distal metaphyseal bone, disimpaction is performed;
- this is accomplished through an opening in the thin anterior meta-physeal cortical bone, by "booking open" the fracture;
- if there is no fracture in this area, then an anterior window is made 2 cm above the impacted plafond;
- key to disimpaction is to free up the articular fragment through normal cancellous bone, so that impacted fragments do not
break apart (rather they are disimpacted so that they move as a single mass);
- w/ elevator & bone tap, impacted cancellous bone is wedged and tapped down to its anatomic location along the articular cartilage;
- defect that is created with this maneuver will later be filled w/cancellous bone graft;
- Articular Fixation:
- articlar fragments are temporarily held by provisional stabilizing w/K wires;
- permanent fixation may then be achieved w/ cannulated screws or cancellous screws;
- Fixation of Metaphysis to Diaphysis
- references:
- The analysis of the variables, affecting outcome in surgically treated tibia pilon fractured patients.