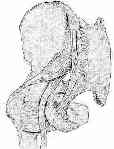
- See: Autograft Discussion
- Technique:
- the middle crest is quite thin and can be easily shattered;
- subperiosteaally, dissect the abdominal musculature and iliacus from the inner wall;
- after the tendinous decussation of the gluteal and abdominal muscles has been incised along the supero-lateral aspect of the crest, create two transverse periosteal incisions across the crest - at both ends of the incision;
- hence the periosteal incisions form three sides of a rectangle;
- one technique involves transversely cutting the iliac crest cap, a distance of 5 mm below the periosteal incision;
- using an osteotome, gently tap thru the medial cortex, preserving the perioteal and abdominal muscle attachments;
- this cap is then reflected medially;
- at this point cancellous bone can be harvested with currettes;
- alternatively, a periosteal elevator can be used to strip the ilacus off the inner table a distance of 5 cm;
- an osteotome is used to create two vertical incisions along the cortical surface of the inner table a distance of up to 5 cm;
- a right angled saw is used to complete the cortical windon;
- disadvantages:
- postoperative ileus may occur in some patients;
- ilioinguinal nerve (supplying sensation to the groin) runs along the medial surface of the iliacus muscle and can sustain a traction injury (neuropraxia) w/ excessive retraction;
- lateral femoral cutaneous nerve runs just below the ilioinguinal, and is also subject to neuropraxia;
- hernia formation: prevented by secure closure of abdominal fascia;
- Post Operative Care:
- as noted by Sasso, et al (1998), there was no apparent advantage or disadvantage to use of drains for iliac crest donor sites;
- reference:
- Postoperative drains at the donor sites of iliac crest bone grafts. A prospective randomized study of morbidity at the donor site in patients who had a traumatic injury of the spine.
Harvesting autogenous iliac bone grafts. A review of complications and techniques.
Fracture at the iliac bone graft harvest site after fusion of the spine.
Bone graft harvest site as a determinant of iliac crest strength.
A technique for obtaining bone graft.
Donor-site morbidity after harvesting rib and iliac bone.
A new technique for obtaining iliac bone grafts.
Procurement of Bone Graft from the Iliac Crest. An Operative Approach with Decreased Morbidity.
Cloward technique for obtaining iliac crest bone graft in hand surgery.