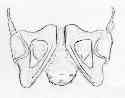
- Discussion:
- diastases: (45%) (may be associated w/ SI ligaments or Malgaigne frx);
- three types of diastases:
- open-book type;
- vertical-displacement type;
- posterior-displacement type;
- straddle fractures;
- straddle frxs (free-floating symphyses) accounted for 20 % of frx;
- > 50% pts had bladder or urethra injury;
- nondisplaced frx require only symptomatic care;
- displaced frx, esp w/ urinary tract injury, require stabilization;
- w/ free-floating symphysis, contraction of abdominal muscles such as that which occurs with coughing produces pain, frx displacement, and soft tissue injury;
- presence of straddle frx should alert for possibility of intr-abdominal or urethral injury;
- 33% of pts w/ straddle fractures required laparotomy;
- intraarticular fractures: (5%)
- mechanism of frx was same in these injuries, consisting of lateral compressive force against pelvis w/ hyperextension or hyper-abduction of the thigh;
- intraarticular frx present no problem in terms of management and usually healed with synostosis of the symphysis;
- overlapping pubic bones are assoc w/ urethral injuries, & residual disability accompanies failure of reduction;
- overlapping dislocations;
- combination fracture-dislocations
- diastases: (45%) (may be associated w/ SI ligaments or Malgaigne frx);
- three types of diastases:
- open-book type;
- vertical-displacement type;
- posterior-displacement type;
- straddle fractures;
- straddle frxs (free-floating symphyses) accounted for 20 % of frx;
- > 50% pts had bladder or urethra injury;
- nondisplaced frx require only symptomatic care;
- displaced frx, esp w/ urinary tract injury, require stabilization;
- w/ free-floating symphysis, contraction of abdominal muscles such as that which occurs with coughing produces pain, frx displacement, and soft tissue injury;
- presence of straddle frx should alert for possibility of intr-abdominal or urethral injury;
- 33% of pts w/ straddle fractures required laparotomy;
- intraarticular fractures: (5%)
- mechanism of frx was same in these injuries, consisting of lateral compressive force against pelvis w/ hyperextension or hyper-abduction of the thigh;
- intraarticular frx present no problem in terms of management and usually healed with synostosis of the symphysis;
- overlapping pubic bones are assoc w/ urethral injuries, & residual disability accompanies failure of reduction;
- overlapping dislocations;
- combination fracture-dislocations