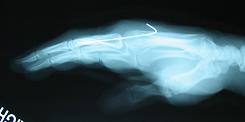
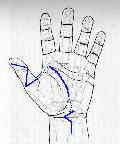
 - See: proximal phalangeal fractures:
- See: proximal phalangeal fractures:
- Disscusion
- indicated for unstable frx of base, shaft, and neck;
- K wire characteristics:
- use 0.035 or 0.045 inch wires, depending on the size of the phalanx
- holding power of the wires:
- increased penetrating ability and holding power with trocar tips, when compared to diamond tips;
- increased holding power w/ lower drilling speeds;
- Technique:
- reduction:
- note that the proximal phalanx has a natural dorsal apex curve and that any K wire IM technique will have a tendency to straighten out
the phalanx (which tends to give a volar apex deformity);
- apply longitudinal traction across the PIP joint as the MP joint is flexed to 60 deg and the PIP joint is flexed to 45 deg;
- ensure that that clinically there is no rotational deformity, and then confirm frx reduction w/ flouroscopy;
- fixation:
- trans-MP joint fixation:
- most indicated for fractures proximal to the midline;
- allows early PIP joint motion (which is the joint that tends to remain most stiff post op);
- MP joint is flexed to 60 deg, and insert a percutaneous K wire longitudinally across metacarpal head to pass down the meduallary canal of the proximal phalanx to
end just shy of the subchondral surface of the condyle;
- ensure that the wire is inserted along one side of the extensor tendon, through the metacarpal head (to pass across the MP joint);
- becuase this technique is technique is difficult, consider initial retrograde K wire insertion thru the distal phalangeal condyle (requires maximal PIP
joint flexion during insertion), which is then driven across the flexed MP joint;
- the K wire is then pulled proximally until its end clears the distal condyle;
- in the reprot by Hornbach, et al, the authors report the results of 12 unstable extraarticular fractures of the proximal
phalanx treated with transarticular intramedullary Kirschner wires;
- early proximal IP joint motion was allowed and all patients achieved uneventful union, with an average total active motion of 265°;
- excellent results were observed in ten of the 12 patients;
- ref: Closed Reduction and Percutaneous Pinning of Fractures of the Proximal Phalanx.
- w/ distal neck frx, consider insertion of 2-3 0.028 inch intramedullary K wires;
- wires may be best inserted down the medullary canal by hand w/ use of T handle device;
- Post Op:
- well padded dressing is then applied to protect the pin sites, but it is important that there remains some PIP motion;
- PIP motion will help to impact frx fragments;
- generally, cast is left on for 3 weeks
Closed Reduction and Internal Fixation of Proximal Phalangeal Fractures.
Percutaneous screw treatment of spiral oblique finger proximal phalangeal fractures.