
- External Fixation
- ref: External fixation of pediatric femoral fractures.
- IM Nailing: (flexible vs rigid)
- avascular necrosis is a reported complication in young adolescents;
- consider IM entry point anterior to piriformis fossa;
- children w/ coxa valga may be at risk for AVN, and it may be difficult to gain entry into the IM canal without damaging the trochanteric physis
- Twenty-Year Experience with Rigid Intramedullary Nailing of Femoral Shaft Fractures in Skeletally Immature Patients
- Impact of Clinical Practice Guideline on the Treatment of Pediatric Femoral Fractures in a Pediatric Hospital
- Traction
- Femoral Traction Pins
- from 10 to 15 yrs, consider 90/90 skeletal traction;
- in this age group, skeletal traction is usually needed to achieve satisfactory alignment and minimize the overiding of the frx fragments
until callus forms at about 3 weeks;
- after 3 weeks apply Spica Cast:
- potenial for shortening is greater in this age group, & further the potential for growth acceleration is much declined;
- union requires 6 weeks;
- after age 15 treat like an adult;
- ref: Skeletal traction for fractures of the femoral shaft in children. A long-term study.

- Anterior Angulation:
- occurs if femur is not flexed in the Spica Cast:
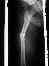
- Varus Angulation:
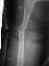
- Wedging the Cast:
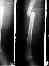
- Telescoping at the Frx Site:
- common complication;
- may be avoided by incorporating femoral traction pin into the spica;
The "floating knee" in children.

