- See:
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
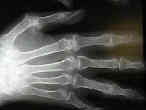
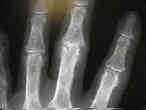
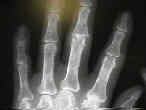
- Rheumatoid Hand
- RA Disease in the Wrist
- Discussion:
- tenosynovitis may present w/ difficulty w/ active PIP flexion, carpal tunnel symptoms, trigger finger, & deQuervain's syndrome;
- tenosynovitis will manifest as dorsal wrist swelling and may be isolated or may occur w/ extensor tendon rupture, and/or carpal arthritis;
- unlike joint synovitis, tenosynovitis predictively gives goods results and should performed early on in the disease process, before tendon ruptures occur;
- indications:
- may be indicated for painful localized synovitis that is not responsive to medical therapy;
- uncontrolled synovitis for 6 months;
- failure of medial therapy, steroid injection, & splinting;
- Extensor Tendon - Tenosynovectomy:
- dorsal tenosynovitis is usually painless, and the mass usually moves with the tendons;
- this is a procedure with predictably good results (unlike joint synovectomy);
- prophylactic extensor tenosynovectomy may prevent extensor tendon rupture;
- incision: straight longitudinal (no S shaped incisions);
- keep flap thick down to the retinaculum;
- management of the retinaculum:
- anatomy: retinaculum is 3 cm in width, and contains 6 extensor compartments;
- within each compartment the extensor tendons are covered by tenosynovium;
- the proximal and distal borders of the retinaculum are defined and are incised transvesely;
- longitudinal incision is typically made thru the 6th compartment (ECU)
- the extensor retinaculum is then elevated towards the radial side, w/ care to avoid injury to the tendons as the 5th, 4th, and 3rd extensor tendons are entered;
- at this point the synovectomy is performed, w/ care to remove synovium from each tendon;
- any extensor tendon ruptures should be identified and managed as appropriate;
- the wrist joint may be opened longitudinally inorder to complete the synovectomy;
- retinacular closure:
- often there will be a tendency for ECU subluxation;
- consider spliting the retinaculum transversely down the middle and placing one half underneath the ECU (as well as the other tendons) and placing the other half over the ECU (and other tendons);
- postoperative care:
- hand should be splinted in extension;
- Flexor Tendon - Tenosynovectomy:
- see: flexor tendon rupture:
- flexor synovectomy, as on the extensor side, can be of benefit in pts w/ boggy flexor synovium;
- Wrist Synovectomy:
- MCP/PIP synovectomy (combined w/ intrinsic release at MCP) & extensor tendon relocation may allow temporary correction;
- synovectomy requires that disease is well controled, no fixed deformity, and minimal radiographic disease in the radiocarpal joint;
- generally joint synovectomy does not yield as predictable results as tenosynovectomy;
- following synovectomy, normal synovium will initially regenerate only to be followed by appearance of rheumatoid synovium
Treatment considerations in the complicated rheumatoid hand.