Skip to content
Discussion
acute arthritis caused by CPPD crystal-induced inflammation;
almost as common as gout & may perfectly mimic gout during acute flare;
pseudogout attacks occurring before age 50 are uncommon;
see: pseudogout occurence after joint replacement
references:
differential diagnosis Clinical Features
most often affects the knee and the wrists;
CPPD Crystal Exam
Crystal Examination of Synovial Fluid :Calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystals are visualized under compensated polarized light microscopy
crystals may be more difficult to detect than MSU crystals because of their smaller size, more intraphagolysosomal location, & less brilliant colors;
in contrast to MSU crystals, CPPD crystals show weak positive birefringency and have squared or rhomboidal shaped ends;
aggregates do not show birefringence (or are weakly birefringent) under polarized light;
alizarin red stain, can confirm that these clumps are masses of calcium crystals;
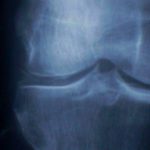
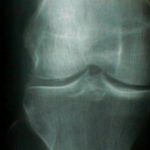
Radiographic Analysis
punctate and linear densities in hyaline or fibrocartilage , which are found in knee menisci, acetabular labrum, & TFCC ;
Therapeutic Principles
aspiration of joint and steroid injection, once diagnosis of infection has been excluded, will usually control symptoms;
indomethacin ;colchicine ? may be useful for pseudogout;magnesium on an as needed basis
arthroscopic lavage:
References