- See: Deltoid Ligament Injuries due to Ankle Fractures
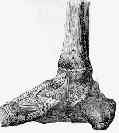
- Anatomy and Function:
- medial side of ankle is stabilized by deltoid ligament, which always has: tibionavicular, tibiospring, and deep posterior tibiotalar ligaments
- superficial deltoid:
- originates from anterior & inferior aspects of medial malleolus fanning out & sending 3 bands to navicular and along plantar
calcaneonavicular (spring) ligament, to sustenaculum tali of calcaneus, & to medial tubercle;
- superficial deltoid lig primarily resists eversion of hindfoot;
- tibionavicular portion suspends spring lig & prevents inward displacement of head of talus, while tibiocalcaneal portion
prevents valgus displacement.
- superficial deltoid is also partially covered by tendon sheaths & crural fascia;
- deep deltoid ligament:
- originates on posterior border of anterior colliculus, intercollicular groove, & posterior colliculus;
- it is oriented transversely & inserts into entire nonarticular surface of medial talus;
- deep deltoid extends function of medial malleolus & prevents lateral displacement of talus & prevents external
rotation of the talus;
- latter effect is pronounced in plantar flexion, when deep deltoid tends to pull talus into internal rotation;
- originates from inferior & posterior aspects of medial malleolus and inserts on medial and posteromedial
aspects of the talus;
- Physical Exam:
- eversion test;
- in neutral evaluates superficial deltoid ligament complex;
- external rotation stress test evaluates syndesmotic ligaments and additionally - the deep deltoid ligament;
- Fractures w/ Deloid Injury:
- see: deltoid ligament injuries due to ankle fractures
- Radiographic Diagnosis of Injury:
- deloid is usually avulsed from tibial attachment, frequently w/ small flake of bone visible on x-rays;
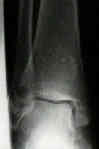
- disruption of deltoid ligament can be dxed w/ relative confidence when medial clear space between talus & med malleolus is increased;
- lateral shift of talus, w/ incr medial joint space ( > 3 mm), but this may be apparent only on stress view or in postcasting films, after swelling has subsided;
- presence of medial tenderness & > 5 mm of space is seen then there is substantial injury of deltoid ligament;
- Treatment of Deltoid Tear:
- such injuries should be rxed as bimalleolar frx, w/ ORIF of lateral malleolus;
- routine exploration of medial side of ankle is not necessary unless there is evidence that portion of deltoid lig has entered joint & is blocking reduction of talus
The deltoid ligament. An evaluation of need for surgical repair.
The medial collateral ligaments of the human ankle joint: anatomical variations.
Anatomical reconstruction of the spring ligament using peroneus longus tendon graft
Deltoid Ligament Repair vs. Syndesmotic Fixation in Bimalleolar Equivalent Ankle Fractures.

