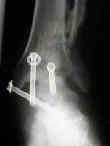
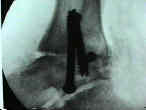
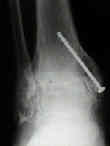
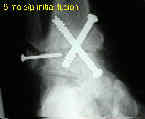
Sub-Talar Fusion
Tibial-Talar-Calcaneal Fusion
- Discussion and Outcomes:
- optimal position for fusion
- see gait and role of ankle joint in gait
- ref: Ankle arthrodesis. Long-term follow-up with gait analysis.
- Exam:
- perform an Allen test for the foot vasculature;
- note function of posterior tibial pulse while the dorsalis pedis pulse is occluded and vice versa;
- check external rotation of ipsilateral hip, since ankle fusion patients tend to hold their lower limb in external rotation in order to
progress through stance phase of gait;
- note amount of subtalar and transtalar mobility, since this correlates with better postoperative functional scores and satisfaction;
- ref: Arthrodesis of the Ankle: A critical analysis.
- Radiographic Studies:
- MRI may be used to judge the vascularity of the talus;
- it may be wise to image the subtalar joint to ensure that there is not concomitant arthritis;
- ref: A roentgenographic technique to evaluate and document hindfoot position.
- Non Operative Treatment Options:
- prior to ankle arthrodesis, the patient should be given the option of wearing either a below knee cast or CAM walker;
- a good candidate for ankle arthrodesis is a patient with documented ankle arthritis, who has obtained pain relief from a CAM
walker, and who does not wish to wear a CAM walker for a lifetime;
- patients can use a double upright AFO w/ a patellar tendon bearing support which partially unload ankle joint during gait;
- adding a rocker bottom orthosis to the shoe will improve transition throughout stance phase;
- Open Exposure for Ankle Fusion:
- alternative techniques: (Blair fusion, compression arthrodesis)
- Arthrscopic Arthodesis:
- requires correctable deformity;
- technique:
- ankle arthroscopy
- use standard knee arthroscopy arthroscope (4 mm) and 4.5 mm burr;
- ankle distraction apparatus:
- remove entire articular cartilage (including medial and lateral gutters) w/ relative preservation of subchondral bone;
- drill multiple holes through the subchondral layer;
- references:
- Safety and efficiency of posterior arthroscopic ankle arthrodesis.
- Anatomic Feasibility Study of Posterior Arthroscopic Tibiotalar Arthrodesis.
- internal fixation w/ cannulated screws:
- screws are inserted inorder to best address direction of deformity;
- with anterior subluxation of the talus, then posterior to anterior screw (posterior malleolus to anterior talar head) is inserted
first followed by screws through the medial malleoulus into the talar body;
- w/ minimal deformity, consider two screws inserted from medial distal tibia into talar body;
- whether fibula needs to be included into the fusion is controversial;
- references:
- Ankle arthrodesis. A comparison of an arthroscopic and an open method of treatment.
- Arthroscopic ankle arthrodesis.
- Arthroscopic ankle arthrodesis in rheumatoid arthritis.
- Arthroscopically assisted arthrodesis for osteoarthrotic ankles
- Long-term results of arthroscopic ankle arthrodesis.
- Arthroscopic Versus Open Ankle Arthrodesis: A Multicenter Comparative Case Series
- Outcomes of Total Ankle Replacement, Arthroscopic Ankle Arthrodesis, and Open Ankle Arthrodesis for Isolated Non-Deformed End-Stage Ankle Arthritis.
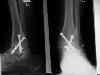 - Internal Fixation w/ Cannulated Screws
- Internal Fixation w/ Cannulated Screws
- External Fixation:
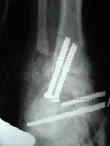
- can be applied to medial surface of the tibia (2-3 pins) and talus (2 pins);
- references:
- Arthrodesis of the ankle with modified distraction-compression and bone-grafting.
- Ankle arthrodesis. A comparison of internal and external fixation.
- Ankle arthrodesis with the Calandruccio frame and bimalleolar onlay grafting.
- Revision of ankle arthrodesis with external fixation for non-union.
- External fixation arthrodesis of the ankle joint following trauma.
- Bone Grafting
- bone graft can be applied to all corners of the fusion, especially between the medial malleolus and talus;
- one option is to insert the first long threaded cannulated screw across the joint, and to observe ankle distraction that occurs
as threads just reach the far surface;
- while the joint is distracted, inject bone graft material evenly across the interval;
- references:
- Locally generated bone slurry accelerated ankle arthrodesis.
- Use of demineralized bone matrix in ankle/hindfoot fusion
- Survey on the need for bone graft in foot and ankle fusion surgery.
- The Importance of Sufficient Graft Material in Achieving Foot or Ankle Fusion
- Post operative management:
- note that even rigid fixation, 8 deg of flexion-dorsiflexion and 7 deg of torsional motion may occur;
- avg immobilization time until all casts are removed is 7-8 months;
- allow unprotected wt-bearing only after bone trabeculation is seen across osteotomy site;
- anteromedial portion of distal tibia undergoes cyclic tension and compression during walking;
- tension in anteromedial tibia occurs after heel strike, & compression occurs after heel off;
- reverse of this cycle would be expected to occur in the posterolateral aspect of the tibia;
- walking does not provide uniform compression across an ankle arthrodesis site, and probably should be avoided until there is
trabeculation across frx site;
- SACH will cushion impact of initial ground contact and help permit initiation for rocker bottom type action during ground contact
in pts who have lost ability to plantar flex from heel strike to foot flat;
- rocker sole helps tibia pass over foot w/ platar flexion from foot flat to liftoff;
- patients with greater tarsal mobility will have better postoperative foot mobility and higher satisfaction;
- Heel-to-toe Rocker Sole
- sole is shaped with an accentuated rocker angle at both the heel and toe
- increase propulsion at toe-off, decrease pressure on heel strike, and reduce the need for ankle motion;
- this type of heel is also useful for patients with severe claw toes, and those with heel ulcers
- Complications of Ankle Arthrodeses:
References:
Salvage of nonunion following ankle arthrodesis for failed total ankle arthroplasty.
Revision arthrodesis for tibiotalar pseudarthrosis with fibular onlay-inlay graft and internal screw fixation.
Compression arthrodesis of the ankle. Evaluation of a cosmetic modification.
Transfibular compression arthrodesis of the ankle joint.
Arthrodesis of the ankle with free vascularized autogenous bone graft. Reconstruction of segmental loss secondary to osteomyelitis, tumor, or trauma.
Arthrodesis of the diabetic neuropathic ankle joint.
Arthrodesis of the Ankle: a critical analysis.
Outcome after single technique ankle arthrodesis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
Arthrodesis of the ankle in patients who have rheumatoid arthritis.
Clinical outcome of tibiotalar arthrodesis utilizing the chevron technique.
Motion Versus Fixed Distraction of the Joint in the Treatment of Ankle Osteoarthritis: A Prospective Randomized Controlled Trial
Batchelor's extra-articular subtalar arthrodesis. A report on sixty-four procedures in patients with poliomyelitic deformities.