- Discussion:
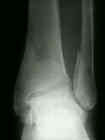
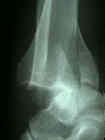
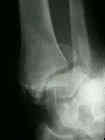
- medial malleolar frx result from direct impact of talus or from tension as talus rotates or moves laterally following fibula;
- in children medial malleolus frx may represent supination inversion frx;
- injury patterns:
- deep deltoid ligament may be torn, leaving malleolus intact;
- anterior colliculus may be avulsed by superficial deltoid, leaving deep deltoid ligament either intact or ruptured;
- frx above level of the ligamentous attachment leaves deltoid ligament attached to the distal malleolar fragment;
- associated injuries: (w/ "isolated" medial malleolar fractures)
- maisonneuve fracture;
- talus neck fracture;
- cuboid fracture;
- deltoid ligament injuries arising from ankle frx
- Radiographic Studies
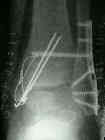
- usually distal frag of medial malleolus is displaced anteriorly & distally;
- eval for osteochondral;
- r/o frx of talar neck;
- Non Operative Treatment:
- Conservative treatment of isolated fractures of the medial malleolus.
- Nonoperative treatment of the medial malleolus in bimalleolar and trimalleolar ankle fractures: a randomized controlled trial.
- Surgical Treatment:
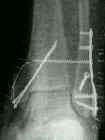
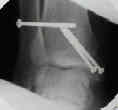
- screw fixation: vertical malleolar frx 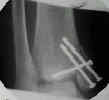
- screw fixation: horizontal-oblique frx
- comminution:
- if medial malleolus is fractured in coronal plane or is comminuted, screw purchase may be difficult;
- small, one third tubular plate can be contoured to run along anterior, distal, & posterior edges of malleolus;
- individual fragments can also be reduced & fixed with a single K wire;
- series of figure of 8 wires can then be placed around these K wires to secure the fragments;
- impaction of articlar surface should be elevated during reduction;
- bone grafting may be needed;
- avulsion fractures:
- avulsion frx of medial malleolus may be treated closed if isloated, minimally displaced, & involve distal portion of malleolus;
- reduced after exposing both the anterior and medial aspects of frx by sharply turning back the periosteum and attached fascia;
- short screw theory:
- better fixation with shorter 30 mm partially threaded cancellous screws which engage the physeal scrar;
- ref: Screw fixation of medial malleolar fracture. A cadaveric biomechanical study challenging the current AO philosophy
- bicortical fixation screws:
- Lag screw fixation of medial malleolar fractures: a biomechanical, radiographic, and clinical comparison of unicortical partially threaded lag screws and bicortical fully threaded lag screws.
- Comparison of pullout strength between 3.5-mm fully threaded, bicortical screws and 4.0-mm partially threaded, cancellous screws in the fixation of medial malleolar fractures.
- Medial malleolar fractures: a biomechanical study of fixation techniques.
- Bicortical fixation of medial malleolar fractures: a review of 23 cases at risk for complicated bone healing.
- tension band technique:
- Ostrum and Litsky, tension band wiring has better mechanical properties than 2 cancellous screws (4 times stiffer than two screws);
- bone fragment is held in reduced position w/ tenaculum clamp;
- two 0.45 K wires are driven thru deltoid ligament and tip of medial malleolus and across frx site, but not into proximal tibial cortex;
- tension band figure of 8 wire (20 gauge) can be anchored proximally thru an anterior to posterior drill hole in m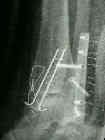 etaphysis (or
etaphysis (or
by wrapping wire around head of the screw placed oblique in metaphysis);
- 20 gauge wire is then passed around the K wires and tightened in a figure of 8 fashion (double twist technique is more reliable);
- K wires are cut and turned medially and then tapped into the bone;
- references:
- Technical Tip: Fixation of Medial Malleolar Fractures Using a Suture Anchor
- Tension band fixation of medial malleolus fractures.
- Modified tension band wiring of medial malleolar ankle fractures
- Comparison of tension band wire and cancellous bone screw fixation for medial malleolar fractures
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Hardware in the medial malleolus: is it intra-articular?
Safe Zone for the Placement of Medial Malleolar Screws.
Medial Malleolar Fractures: A Biomechanical Study of Fixation Techniques