- See: Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Pathoanatomy:
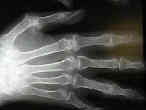
- RA Disease in the Wrist
- Extensor Tendon Rupture
- Tenosynovitis
- diff dx: w/ RF negative tenosynovitis consider myobacterium marium infection;
- Flexor Tendon Rupture
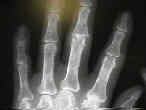
- Ulnar drift
- MP joint
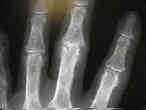
- PIP Joint
- Boutonniere
- Swan Neck Deformity
- Thumb Deformities
- Intrinsic Contracture
- approximately 40% of pts w/ RA will have intrinsic contracture;
- typically in RA, the ulnar sided intrinsics will contract more than the radial intrinsics, leading to ulnar drift;
- in some cases the intrinsic contracture will result from MP joint dislocation, and in other cases, the intrinsic contracture will be idiopathic (and may result in MP dislocation);
- as the intrinsic tightness progresses (as determined by Bunnel test), either MP subluxation will occur or the constant pull of the intrinsics will cause a swan neck deformity beginning at the PIP joint;
- when MP subluxation occurs, tension will be taken off the intrinsics, which then allows full PIP flexion when the MP joint is extended;
- when MP joint is reduced, the severity of the intrinsic contracture will be noted, as reflected by loss of PIP flexion;
- management:
- when intrinsic contracture is noted in early stages (prior to MP subluxation or swan neck deformity), consider release of the insertions of the ulnar intrinsics which includest the lateral bands and their fascial connections (oblique and transverse fibers);
- Littler release: releases the intrinsic distal to the MP joint, and should only be performed if full passive extension of the MP joint is possible;
- Zancolli release: release at the MT junction of the intrinsic muscle, and releases the intrinsic from the proximal phalanx;
- Work Up:
- lab studies
- radiographs
- Treatment:
- non operative treatment;
- operative treatment:
- operative treatment is based on presence of specific deformities:
- tenosynovectomy may prevent extensor tendon rupture;
- extensor tendon rupture
- tenosynovitis
- flexor tendon rupture
- ulnar drift
- MP joint
- PIP Joint
- boutonniere
- swan neck deformity
- thumb deformities
- intrinsic contracture
Extensor digiti minimi tendon transfer to prevent recurrent ulnar drift.
Treatment considerations in the complicated rheumatoid hand.